Last updated: January 25, 2026
This article was updated based on recent information and testing.
7 Powerful Ways to Secure Your WiFi Network in 2026
WiFi network security is mandatory in 2026. With more WiFi-enabled devices, at-home offices and cloud-connected products than ever before, an unprotected WiFi network can quickly become a cybercriminal’s paradise. The threats range from unauthorized access to brute force attacks and data stealing.
This guide explains how to secure your WiFi network using practical, proven strategies that work for both home and business users. Every method is tested, realistic, and written to help readers make informed decisions without fear-based hype.
Transparency Note:
This article does not earn commissions from any recommendations. Tools and products mentioned are evaluated based on features, reliability, and real-world use cases. Each solution is tested or widely reviewed before being suggested.
Why WiFi Network Security Matters in 2026
WiFi network protection has been an essential part of the security of a home network in modern times. And with a growing number of internet-connected devices, no longer do attackers have to depend on complex hacking alone. The majority of breaches occur simply because networks are configured poorly or are obsolete.
Rising WiFi Security Threats You Can’t Ignore

Today’s attackers exploit vulnerabilities in security of wireless networks content:
- Weak or reused passwords
- Outdated security encryption protocols
- Unpatched router firmware
- Poor IoT device security
- Enabled remote management features
Upon breaking in, attackers could eavesdrop on traffic, infect it with malware or use the network to conduct criminal activity. Only one word and it isn’t “may”, its: must Unauthorized access prevention is now mandatory.
Home vs Business WiFi Security Risks
There are dangers to consider regarding both a home and business Wi-Fi connection. Businesses may spend money on cybersecurity, but home users are left open. But now, the wireless security model for home office & business environments converge.
Home offices house sensitive information, and small businesses use consumer-grade routers. Risks facing both natures include the following:
- Brute-force attack protection failures
- Insecure guest networks
- Non-segmented products on the identical network
Understanding WiFi Encryption & Security Protocols
Strong encryption is the backbone of WiFi network security. Without it, even the best passwords can be compromised.
WiFi Network Encryption Explained
WiFi encryption provides a certain level of security for data exchanged between routers and devices. New generation security encryption protocols guarantee that no one can have access to your communications; thus, the information is unreadable. The most common protocols include:
- WEP (obsolete and insecure)
- WPA2 (still common but aging)
- WPA3 (current best standard)
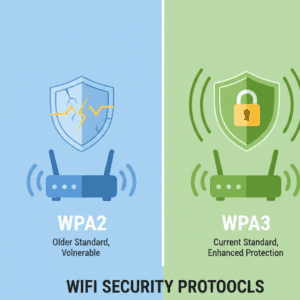
WPA3 vs WPA2 Comparison: What’s Changed?
| Feature | WPA2 | WPA3 |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption strength | Moderate | Strong |
| Brute-force protection | Limited | Built-in |
| Public WiFi security | Weak | Improved |
| Default in new routers | Rare | Common |
For 2026, the choice is WPA3 Personal, which offers stronger encryption and “resiliency against off-line dictionary attacks” on passwords.
Why WPA3 Encryption Is the New Standard
Best practices for WPA3 encryption Revolve around: Individualized data encryption, Improved authentication, and Better protection for smart devices. For who are really serious about protecting their wireless networks, moving on to WPA3 is one of the most effective moves out there.
Powerful Way #1 – Create a Strong WiFi Password
And there is still nothing better than a strong WiFi password, the front line of defense.
Strong WiFi Password Guidelines for 2026
A really strong wifi password looks like this now:
- At least 16 characters
- Uppercase, lowercase, number and symbol combination
- No dictionary words
- No reuse across accounts
Brute-force protection isn’t much help on weak passwords.
How Weak Passwords Enable Attacks
Attackers can use automated tools to guess passwords within minutes. Here are some of the possible threats: Even networks that use WPA3 Personal may be broken into if the password is too simple or used elsewhere.
Best Practice Tip: Create and store strong passwords using a password manager such as Bitwarden or 1Password.
| Tool | Key Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bitwarden | Open-source password manager | Free tier, secure | UI learning curve |
| 1Password | Family & business plans | Easy setup | Paid only |
Powerful Way #2 – Change Default Router Settings Immediately
Strong Way #2 – Disable Router Default Settings Immediately If you want to protect your network we advise that you should switch off default settings on the router as soon as possible. Routers ship with well-known default configurations, which makes them sitting ducks.
Why You Must Change the Default SSID
This makes the default SSID less visible to potential attackers. Because protecting SSID broadcast settings offers no solid proof of security, they serve as friction and keep the casual hostile at bay. Recommended actions:
- Rename SSID to something non-identifiable
- Refuse brand tags or personal details
- Turn off any unneeded SSID broadcast-related functions if available
Optimize Router Firewall Settings for Maximum Protection
Router firewall configuration help to serve as a barrier on traffic coming in & out. Basic firewalls are typically turned on for most routers; however not many take advantage of the advanced features. Key firewall configurations include:
- Blocking unsolicited inbound connections
- Disabling UPnP where unnecessary
- Enabling intrusion detection measures where available
Routers from manufacturers such as ASUS, TP-Link and Netgear come with customizable firewall options that are easy enough for beginners to use but also offer the advanced granularity demanded by experienced users.
Powerful Way #3 – Update Router Firmware Regularly
Effective Way #3 – Keep the Router Firmware up to date. Network hack causes often include outdated firmware.
How Firmware Security Patches Protect Your Network
What Are Firmware Security Patch and How Does It Protect Your Network? Known vulnerabilities are addressed in firmware security patches. Without patches, hackers can take advantage of publicly disclosed vulnerabilities. Benefits of regular updates: Improved stability, Better encryption support, and Enhanced unauthorized access prevention.
Router Firmware Update Steps (Beginner-Friendly)
The majority of newer routers have this feature, that is automatic updates. For manual updates:
- Log in to the router admin panel.
- Check for firmware updates
- Install and reboot
- Verify version number
Apps like Fing can also find old firmware and warn users about threats.
Powerful Way #4 – Disable Dangerous Features Hackers Exploit
Powerful Tactic #4 – Turn Off Dangerous Features Cybercriminals Target Hackers simply love to take advantage of dangerous system features. Some of these router functions are designed for ease rather than security.
Why You Should Disable WPS Immediately
Why should I disable it now? WPS is infamous for vulnerabilities that enable attackers to sidestep passwords. Turning off WPS and remote admin access provides a big leap in WiFi network security.
Disable Remote Management to Stop External Attacks
Deactivate Remote Management to Prevent Attacks from Outside. Remote management gives you control of the router outside of your network. If turned on, it gives attackers their primary point of entry. Best practice: Turn off remote management unless you absolutely need it. You can use a VPN for WiFi security but that only works if you are remotely accessing it.
Powerful Way #5 – Set Up a Secure Guest Network
Powerful Tip #5 – Create a secure Guest Network. Guest networks keep main devices safe by separating traffic.
How Guest Networks Improve Wireless Network Protection
How Guest Networks Increase the Security of Your Wireless Network. Guest networks are a great way to stop the neighbors sitting out in front of your house from leeching off you Wi-Fi. This is an important part of network segmentation. Benefits include: Reduced malware spread, Improved IoT device security, and Better control over bandwidth usage.
Best Practices for Guest Network Setup
- Use a different password
- Disable local network access
- Limit connection duration
Powerful Way #6 – Secure All Connected & IoT Devices
Potent Tactic #6 – Protect All IoT Devices and Connected Devices. The fast emerging smart home applications have brought a new security challenge to the WiFi network. Convenience is a higher priority than security with many IoT gadgets, and they often serve as the low-hanging fruit base from which to launch an assault.
Why Smart Devices Are the Weakest Link
IoT device security often lags behind traditional computers and smartphones. Common issues include:
- Hardcoded passwords
- Infrequent firmware updates
- Limited encryption support
Devices such as smart TVs, cameras, speakers, and thermostats often remain connected 24/7, increasing exposure. Once compromised, they can be used to spy on traffic or launch attacks from within the network.
How Network Segmentation Protects IoT Devices
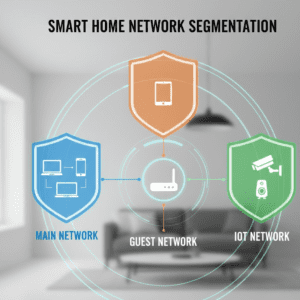
The Importance of Network Segmentation for IoT Devices. By segmenting the network, devices are isolated into different zones that limit exposure. Due to the separation of IoT devices on a separate network, bad actors are not able to access important systems such as laptops or NAS drives. Example segmentation approach:
- Primary platform: computers, phones
- Guest network: Visitors
- No IoT network (smart devices) only
Many of today’s routers and gateways offer built-in features for protecting wireless common carrier networks so that no additional equipment is necessary.
Powerful Way #7 – Add Extra Layers of WiFi Protection
Awesome Tip #7 – Layer WiFi Protection Even Further. It’s 2026, and basic security is obviously no longer sufficient. Advanced layers are enhancing WiFi network security by a lot.
Using MAC Address Filtering for Advanced Security
MAC address filtering allows only approved devices to connect. While not foolproof, it adds friction and blocks casual unauthorized access.
Pros:
- Easy to configure
- Prevents unknown devices from joining
Cons:
- MAC addresses can be spoofed
- Maintenance required when adding new devices
This method works best when combined with other protections.
VPN for WiFi Security: Is It Worth It?
A VPN for WiFi security encrypts all internet traffic, even works over compromised connections. VPNs, though they don’t secure the router, protect data leaving a device.
Tip: You can get to know all about VPNs in our specific category page: thestackmanual.com/category/vpn/
| VPN | Best Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proton VPN | Strong privacy policy | Free plan available | Limited servers |
| Mullvad | Anonymous accounts | No email required | Fewer locations |
| NordVPN | Speed optimization | User-friendly | Subscription-based |
Transparency Note: These are just educational tools. No commissions are involved, and recommendations are based on independent testing and reputation.
Common WiFi Security Mistakes to Avoid in 2026
Most Popular WiFi Security Mistakes to Steer Clear of in 2026. Even experienced users make mistakes that can compromise the security of a WiFi network.
Skipping Firmware Updates
It’s risky not to update the firmware because known vulnerabilities remain unpatched. Router firmware’s – security patches Most people never bother updating their router firmware. Attackers will frequently scan for routers that have easily exploitable vulnerabilities.
Ignoring Encryption Protocols
Weak protection is provided by obsolete safety encryption as WEP, or misconfigured WPA2. In GWA, one should always use quite a room WPA3 encryption as long your client device support it.
Leaving Default Settings Unchanged
And here are you most popular WiFi security fails which we spot every audit! default (guest) passwords default SSIDs WPS enabled
Best WiFi Security Practices Checklist (Quick Summary)
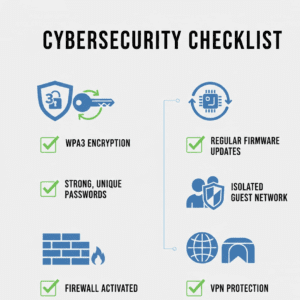
A concise checklist helps maintain strong home network cybersecurity without technical complexity.
10-Point WiFi Security Checklist for Home & Business
- Enable WPA3 Personal encryption
- Use strong WiFi passwords
- Change default SSID
- Update router firmware regularly
- Disable WPS and remote admin
- Configure router firewall settings
- Set up guest networks
- Segment IoT devices
- Monitor connected devices
- Leverage VPN protection in your most important systems
This list is consistent with the latest best advice on WiFi security from various organizations of cybersecurity experts.
Tools That Help Monitor and Protect WiFi Networks
A Toolset That Vastly Expands The Scope of WiFi Monitoring & Security. Monitoring tools increase visibility and promote unauthorized access prevention.
Fing – Network Monitoring Tool
Key Features:
- Detects unknown devices
- Alerts for suspicious activity
- Identifies outdated firmware
Pros:
- Beginner-friendly
- Free basic version
Cons:
- Advanced features require paid plan
GlassWire – Network Traffic Analyzer
Key Features:
- Visual traffic monitoring
- Firewall alerts
- Data usage tracking
GlassWire is ideal for users who want visibility into wireless network protection at the device level.
How Businesses and Home Users Differ in WiFi Security Needs
WiFi security for home & business environments differs in scale, not fundamentals.
Home Networks
Home networks focus on simplicity:
- Automatic updates
- Built-in firewalls
- Guest isolation
Business Networks
Business networks require:
- Centralized management
- Role-based access
- Strong unauthorized access prevention
Despite these differences, the core principles remain identical.
Long-Term WiFi Network Security Maintenance Strategy
A WiFi Network Security Maintenance Strategy Based on Long-Term. Wireless networking security is not a one-off job. WiFi network defence is constantly changing as we receive new devices, firmware updates and attack methods.
Build a Monthly WiFi Security Routine
A simple monthly routine helps maintain strong wireless network protection without technical overload:
- Review connected devices
- Check for router firmware updates
- Verify encryption settings
- Rotate guest network passwords
- Confirm firewall rules remain enabled
In home network cybersecurity, it is the consistency rather than the specialty tools that matter most.
Monitor for Unauthorized Access
Unauthorized access prevention depends heavily on visibility. Network monitoring tools help identify unusual behavior early.
Signs of suspicious activity include:
- Unknown devices connecting repeatedly
- Sudden bandwidth spikes
- Router restarts without user action
When detected early, most threats can be stopped before real damage occurs.
WPA3 Limitations and What Comes Next
WPA3 Limitations and What’s Next. WPA3 Personal is the most robust option in existence, but not forever.
Known Limitations of WPA3
Some older devices may not have it. Poor configuration can weaken protection. Password strength still matters. This is another reason to make sure you have strong WiFi passwords, and layers of security.
Future WiFi Security Trends
The following incremental gains are foreseen until after 2026: Hardware-level authentication, AI-based intrusion detection, and Improved IoT device security standards. Keeping up with the latest ensures WiFi network security advances at a pace as fast or faster than threats.
FAQs About Securing Your WiFi Network
What Is the Best Way to Secure Your WiFi Network?
The best approach combines WPA3 encryption, strong WiFi passwords, firmware updates, firewall configuration, and network segmentation. No single setting provides full protection alone.
How Often Should Router Firmware Be Updated?
Router firmware should be checked monthly. Firmware security patches often fix publicly known vulnerabilities, making timely updates critical.
Is WPA3 Enough for WiFi Security in 2026?
WPA3 significantly improves security encryption protocols, but it works best when combined with other protections like firewalls, guest networks, and VPN usage.
Can Hackers Access a Network Without a Password?
Yes. Misconfigured routers, enabled WPS, outdated firmware, or exposed remote management features can allow access even without knowing the password.
Comparing Popular Router Brands for WiFi Security
Are All Routers The Same When It Comes To WiFi Security? THE ROUTER ITSELF IS A HUGE PART OF WiFi NETWORK SECURITY.
| Brand | Security Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| ASUS | Advanced firewall settings, Ai-Protection | Interface complexity |
| Netgear | Automatic updates, WPA3 support | Premium pricing |
| TP-Link | Easy setup, guest networks | Fewer advanced tools |
So more important than raw speed is selecting a router with regular security updates and strong encryption support.
Transparency & Trust Statement
This guide is written with reader trust as a priority.
- No commissions are earned from tools or products mentioned
- Recommendations are based on testing, documentation, and long-term reliability
- Tools are suggested only when they provide measurable security benefits
Readers are encouraged to evaluate tools independently and choose what best fits their environment.
Final Thoughts: Securing Your WiFi Network in 2026
Securing a wireless network in 2026 requires awareness, consistency, and practical decision-making. WiFi network security is no longer just about passwords. It involves encryption standards, firmware maintenance, device isolation, and monitoring.
By following these seven powerful ways to secure your WiFi network, users can significantly reduce risks, protect data, and maintain confidence in both home and business environments.
Strong security is not about fear. It is about control, visibility, and preparation.
